(27) Cabecera Taladrinas

Cutting fluids
Industries from the metal sector are amongst the main consumers of industrial oil, which they use as lubricating and cooling fluids in some of their most common operations, such as cutting, molding and mechanical treatment on metals. The main example of this industrial oil use are the so called cutting fluids.(24) Taladrinas (INDUSTRIA). Qué son las taladrinas.
What are cutting fluids?
Cutting fluids are oil and water emulsions. This emulsion has a variable concentration with values close to 5% of oil and 95% of water, depending on the different use. It is a product mainly used in the metal processing industry because of its lubricating and cooling properties in processes with a direct contact between the part to be moulded or transformed and the tool used to do it.
Cutting fluids optimise the physico-chemical conditions in the metal to metal contact area reducing friction thus easing metal surface finish and extending the shelf life of the tool. Additionally, cutting fluids avoid overheating of parts and machinery, drain swarf and prevents rust.
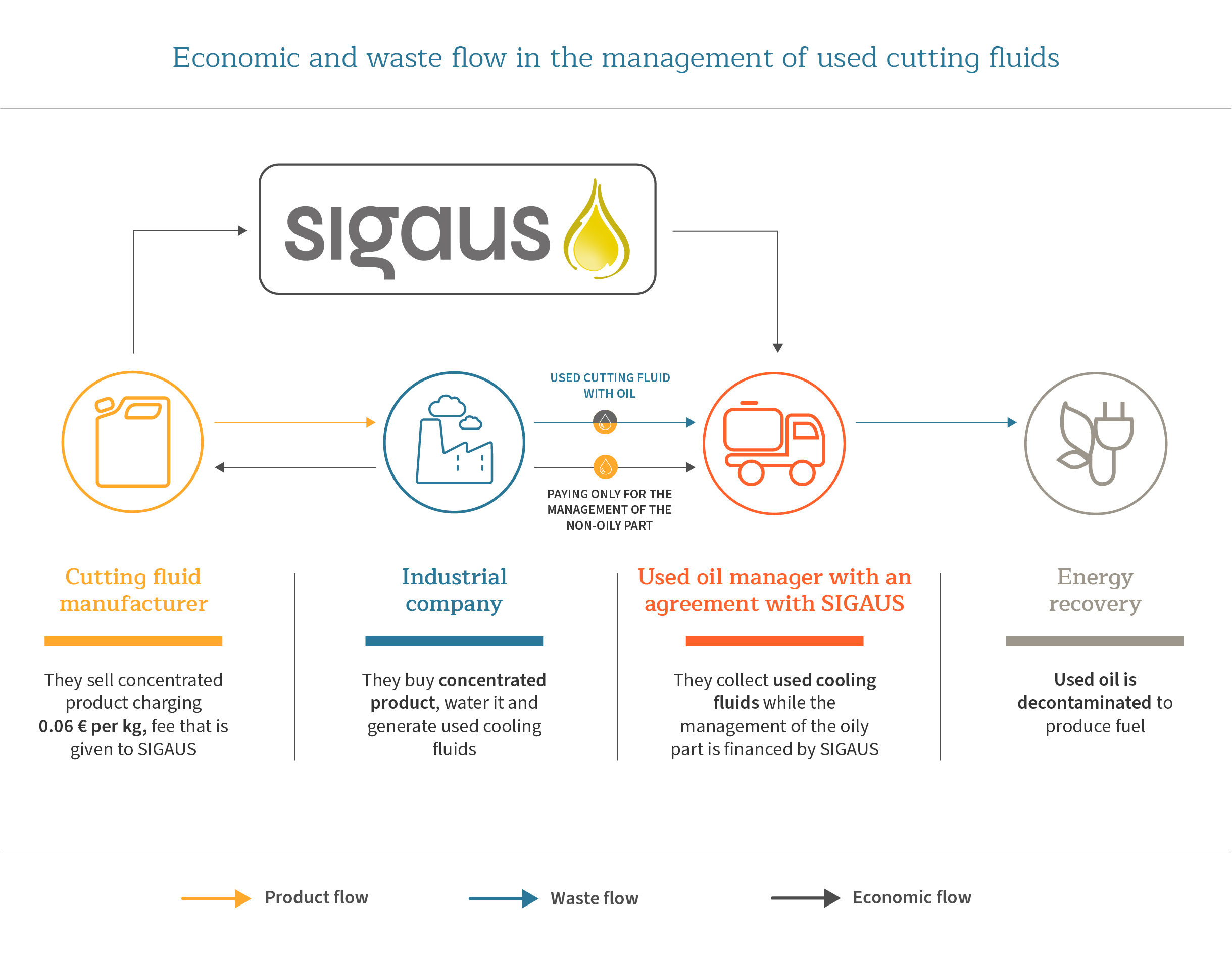
Cutting fluids and other oil used as such are industrial oils and their manufacturers/importers must manage used oil individually or become part of a IMS, and tax the product with the corresponding fee. Consequently, the collection and management of the resulting used oil, such as used cutting fluids, machining mud, degreasing residue, oily water, etc. is covered by the SIGAUS system.
(24) Taladrinas (INDUSTRIA). Qué ocurre con las taladrinas usadas.
What happens to used cutting fluids?
Due to the use and mechanical stress they suffer, the properties of cutting fluids disappear reducing its efficiency and getting contaminated with external agents, such as oil and grease, metal solid particles, microorganisms, dust, etc. This combination of external agents and cutting fluids components, turn these products, once they are used, into a highly hazardous waste, both for the environment and for the operators using them. Used or empty cutting fluids may incorporate heavy metals, biocides, harmful germs and decomposed substances, nitrosamines, boron compound, etc., so they are considered a hazardous waste according to the European and Spanish legislation.
Current legislation forces industry to properly manage this waste. Being this an 'off-spec' oil, due to its percentage of water and sediment, its treatment implies a complex and very costly process so its collection cannot be performed free of charge. It must go through a pretreatment so it can be afterwards managed at the treatment plant. To separate the oily from the watery part, there are several physico-chemical systems that can be applied in physico-chemical plants. The resulting separated oily part is the one that must be managed.
The management of the cutting fluids oily part can be financed through SIGAUS, even if the waste is delivered prior to its separation. For its part, managers that keep a contract with the IMS must take €12 from each tonne of net oil within the managed waste.
(24) Esquema flujos económicos taladrinas. INDUSTRIA
11 - pie taladrinas

Used oil in Spain
Ribadeo. Galicia.Playa de las Catedrales Natural Monument. Biosphere reserve. Ramsar zone for bird protection. More than 20,000 kg of used oils collected and managed in the vicinity of this protection zone.